EMA 630 Viscoelastic Solids Project Ideas
University of Wisconsin
Measure the creep response of polymer foam earplugs. Make an experimental device to do this. It is not difficult.
Calculate the rolling resistance due to the viscoelasticity of the rubber in a tire. Hint: consider the change in stress in the contact patch compared with the rest of the tire.
Use resonant ultrasound spectroscopy to determine viscoelastic properties of a material of your choice. Specimen shape is typically a cube, sphere, or short cylinder.
Calculate from an extrapolation of published data how much height an astronaut will gain during a one month stay on a space station, from viscoelastic recovery of the spinal disks.
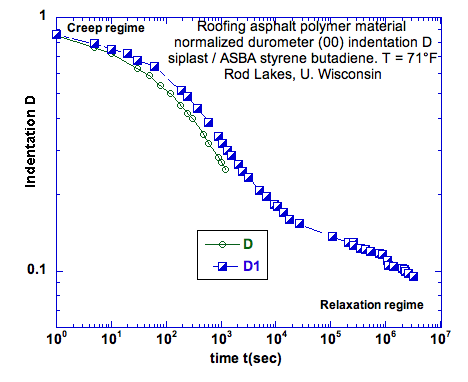
Do indentation testing on the petroleum phase of asphalt and compare with the petroleum phase without any aggregate (stone phase). Would you expect any difference?
Measure the viscoelastic properties of a squash ball, a baseball, a hockey puck, or of a ball used in another sport. How does the actual rebound behavior compare with the rebound predicted based on the measured viscoelastic behavior? How does rebound depend on temperature? Survey the literature on this sport; relate the ball viscoelasticity to the nature and strategy of the sport.
Determine whether polymer foam earplugs are thermorheologically simple by conducting creep tests at several temperatures.
Determine whether polymer foam earplugs exhibit creep due to stress-induced flow of air from the pores according to Biot type theory. What happens if water is introduced in the pores? Does your result depend on the size of the specimen? Specifically, will poro-elastic effects be slower for larger specimens?
Design a viscoelastic system for reducing noise and vibration from a lawn mower or other small engine.
Consider equation 3.68, Viscoelastic Materials . (i) Develop a higher order series expansion to obtain an analytical solution which accounts for the asymmetric resonance peak shapes observed when damping is not sufficiently small that equation 3.80 applies. Does one additional term suffice? Draw plots to compare resonances via equation 3.68 with resonances via its series approximation. (ii) Does your analysis apply for large damping, e. g. tan delta = 0.5? If not, can you extend the analysis to equation 3.68, so that G* is extracted from the complex rigidity?
Referring to example 6.1, (i) develop an explicit series expansion for creep J(t) = A tn,
(ii) derive a corresponding form for nonlinear viscoelasticity following nonlinear superposition, equation 2.102,
(iii) consider what other physical systems to which the analysis applies.
Determine whether viscoelastic shoe insoles offer benefit in reducing impacts during running.
Are viscoelastic mattresses comfortable in relation to their viscoelasticity? Is there any basis to commercial claims?
Indentation creep and relaxation with a spring loaded indenter. Consider Laplace transforms.